Free Clinical Bioinformatics and Genomics MOOC
22 Jun 2017
Explore the world of a Clinical Bioinformatician and their important role in a patient’s journey in this free five week course
The University will deliver the fourth run of its successful 'Clinical Bioinformatics: Unlocking Genomics in Healthcare' massive open online course (MOOC) hosted on FutureLearn starting Monday 26 June.
The course, which has seen 10,000 participants to date, is led by Dr Angela Davies and Professor Andy Brass and has been developed in conjunction with colleagues from the Faculty of Biology, Medicine and Health and the Manchester Centre for Genomic Medicine.
It will illustrate how the discipline of Clinical Bioinformatics provides an important bridge between the cutting edge science and the delivery of genomic medicine in clinical practice. Through a range of case studies and interviews, the learners will experience the world of a Clinical Bioinformatician, bringing sequencing techniques and data analysis processes to life.
The course will run for five weeks, with a new set of learning resources made available each week. Enrolment is free and the course is open to all current practising healthcare professionals who are interested in learning more about the role of Clinical Bioinformatics and will also be applicable to people with an interest in the application of genomics in healthcare. It is not essential to have previous experience or knowledge of Bioinformatics or Genomics, although medical terminology is used.
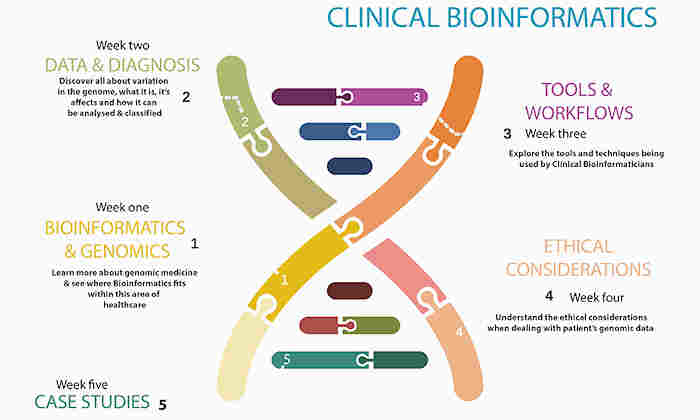
Week 1 - Learn more about genomic medicine and see where Bioinformatics fits in with this area of healthcare.
Week 2 - Data and Diagnosis - discover all about variation in the genome, what it is, its affects and how it can be analysed and classified.
Week 3 - Tools and Workflows - explore the tools and techniques being used by Clinical Bioinformaticians.
Week 4 - Ethical consideration - understand the ethical considerations when dealing with patient's genomic data.
Week 5 - Case studies.
For more information and to register:
